License Management Software:
Tracking and Compliance
Streamline software licensing, ensure compliance, and optimize IT costs with robust license management software solutions.
Software License Management plays a vital role in IT Asset Management. Zecurit Asset Manager makes it easy to track, manage, and optimize your software licenses, helping you stay compliant while cutting down on costs. With a user friendly interface and robust features, you can maintain control over license utilization, renewal schedules, and compliance risks.

Key features of Software License Management
1. Centralized license repository
A well-organized, centralized license repository is truly the backbone of any successful software license management system. By keeping all license-related information in one spot, businesses can effortlessly track, access, and update their software data.
Here are some key components of a centralized repository:
- License names and keys: Information about the specific software licenses, including serial numbers or activation keys.
- Vendor and contract information: Details on the software vendor, licensing agreements, and contract terms.
- Purchase and renewal history: A clear record of when licenses were purchased, and their renewal dates, making it easier to plan for future needs.
- Assigned and unassigned licenses: Clear visibility into which licenses are currently in use and which ones are available, ensuring that there’s no over- or under-provisioning.
Having all this information in one place not only ensures accuracy but also saves time and gives a quick snapshot of the company’s software assets.
2. License utilization insights
Understanding how your software licenses are being used is crucial to optimizing both cost and compliance. A good license management system should offer insights into license utilization, which can help businesses make informed decisions.
Key features include:
- Track assigned and unassigned licenses: Quickly identify which licenses are being actively used and which ones are sitting idle.
- Monitor license utilization rates: Track the number of users per license and ensure that the company is not paying for more licenses than necessary.
- Identify underutilized licenses: By spotting underused software, businesses can reassess their needs and either reassign or eliminate excess licenses, reducing costs.
By gaining a clear understanding of how licenses are being utilized, companies can minimize waste and maximize their return on investment (ROI).
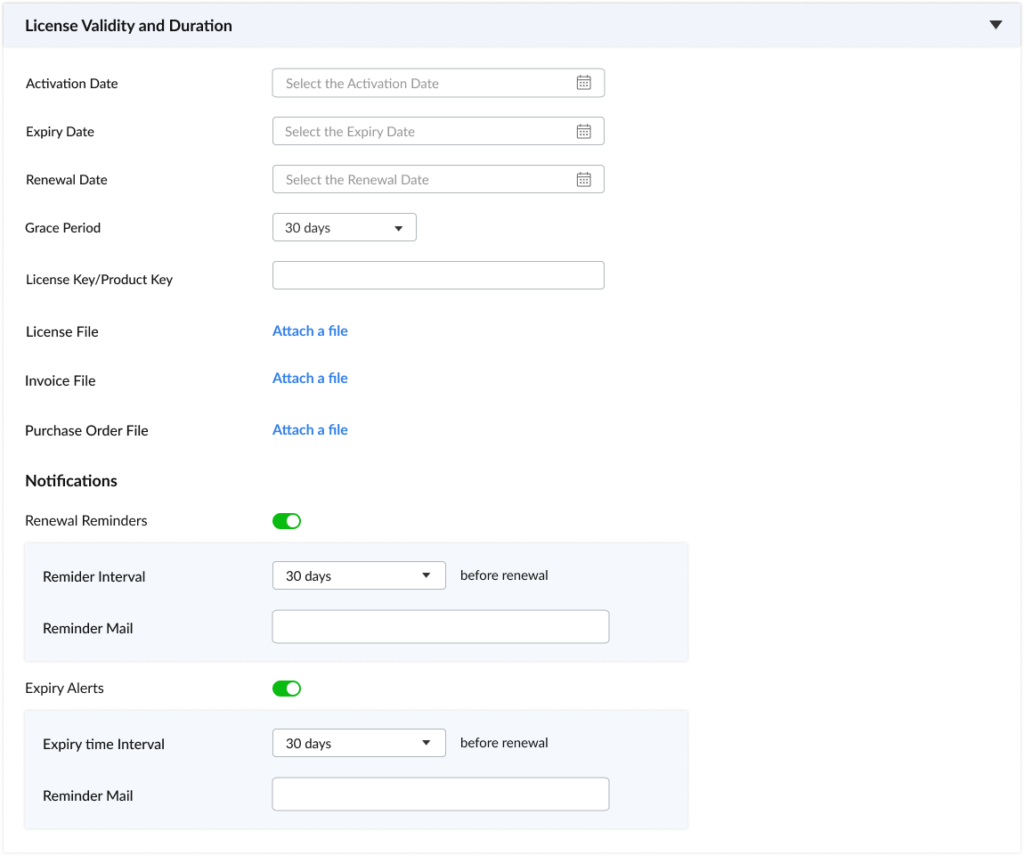
3. Renewal and expiry alerts
One of the most challenging aspects of license management is keeping track of renewal deadlines. Missing a renewal can result in service disruptions, compliance issues, and even penalties. A software license management system helps by sending proactive alerts and reminders.
Key features include:
- Upcoming renewal notifications: Receive reminders well in advance of license expiry dates, giving you ample time to evaluate whether to renew or reassess.
- Days-to-expiry tracking: Monitor the exact number of days left before a license expires to prevent last-minute surprises.
- Auto-renewal status monitoring: Track licenses that are set to auto-renew and ensure that they’re still required or eligible for renewal.
This feature not only helps in staying on top of renewals but also prevents lapses in compliance and service continuity.
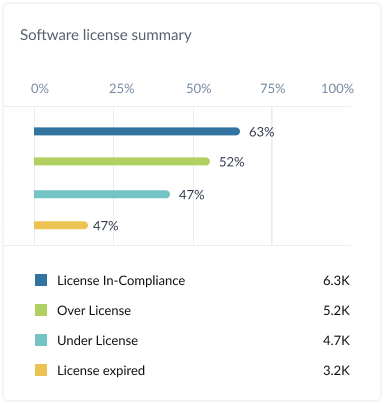
4. Compliance management
Compliance is a significant concern for businesses when it comes to software usage. Violating software license agreements, whether through overuse, unlicensed installations, or geographic restrictions, can result in hefty fines or legal action. Effective software license management ensures that companies stay compliant with all agreements.
Key features include:
- Real-time compliance tracking: Monitor software usage to ensure compliance with licensing terms and conditions.
- Non-compliance alerts: Receive notifications if a license is being overused or if any software is being installed without a valid license.
- Audit-ready reports: Generate detailed compliance reports to assist with internal audits or to be presented during official vendor audits.
By ensuring compliance, businesses can mitigate risks associated with software piracy, overuse, and breach of contract.
5. Financial analysis and cost optimization
Software licenses can be a significant portion of a company’s IT budget. Managing this expenditure effectively requires detailed financial analysis. A well-integrated license management system allows businesses to gain valuable insights into their software spend.
Key features include:
- Total license cost tracking: Keep track of the total cost of all licenses across the organization, including initial purchase costs and ongoing maintenance fees.
- Cost of underutilized licenses: Identify which software licenses are underused or unnecessary, and evaluate their financial impact on the business.
- ROI calculation: Analyze the return on investment (ROI) for each software license by comparing costs against business benefits and usage.
This financial analysis empowers businesses to optimize their software portfolio, eliminate waste, and ensure that they’re getting the most value for their money.
6. Robust reporting capabilities
Effective reporting is essential for making data-driven decisions and ensuring transparency. A strong software license management system should be equipped with robust reporting features that help track and evaluate key metrics.
Common reports include:
- License utilization report: Provides an overview of how many licenses are assigned versus available, and tracks usage patterns.
- Renewal and expiry report: Displays upcoming renewals and expiration dates, making it easier to plan for future renewals.
- Compliance report: Tracks adherence to licensing agreements, helping businesses stay audit-ready.
- Financial analysis report: Offers insights into license costs and ROI, highlighting potential areas for savings.
Having these reports readily available helps businesses make informed decisions about software procurement, usage, and renewals.
7. Intuitive user dashboard
An intuitive dashboard is a crucial feature of a modern software license management system. It serves as the central hub for monitoring key license metrics and accessing critical data quickly.
Features of a user-friendly dashboard include:
- High-level overview: A summary of your entire software license portfolio, including status updates on compliance, renewals, and utilization.
- Quick access to critical metrics: Easily view important information such as upcoming renewals, compliance status, and license usage.
- Customizable widgets: Allow users to personalize the dashboard with widgets that display the most relevant data for their role or needs.
A well-designed dashboard enhances the user experience and simplifies the monitoring of software license data.
8. Multi-level access control
To ensure the security and integrity of license data, businesses need to control who can access and modify sensitive information. Multi-level access control helps maintain data confidentiality and accountability.
Key features include:
- Role-based permissions: Assign specific access rights based on roles (e.g., admins, managers, staff) to ensure that users can only view or edit relevant information.
- Audit logs: Maintain a detailed log of all changes made to the license data, ensuring full transparency and traceability.
By implementing access control, companies can safeguard their license data from unauthorized modifications and track any changes for accountability.
Types of software licenses
Software license management tools are crucial for commercial licenses due to their inherent complexity and the potential for significant legal and financial risks.
1. Proprietary licenses
Perpetual licenses:
- One-time purchase: You pay a single upfront fee for the right to use the software indefinitely.
- Ownership: You don't own the software itself, but you own the right to use it.
- Maintenance: Often requires separate maintenance agreements for updates and support.
- Example: Traditional software like Adobe Photoshop (perpetual versions) or Microsoft Office (legacy versions).
Subscription licenses:
- Recurring payments: You pay a recurring fee (monthly or annually) for the right to use the software.
- Access: Access to the software is typically granted through a subscription portal or cloud service.
- Updates & support: Usually includes regular updates, bug fixes, and technical support as part of the subscription.
- Example: SaaS (Software as a Service) applications like Salesforce, Microsoft 365, and many cloud-based tools.
Named user licenses:
- Assigned to specific users: Licenses are tied to specific named users, regardless of the devices they use.
- Common in enterprise settings: This model is often used in large organizations to control who can access software.
- Example: Enterprise software like some versions of SAP or Autodesk tools.
Concurrent user licenses:
- Limited concurrent use: Allows a fixed number of users to access the software simultaneously, regardless of the total number of users.
- Flexible for shared environments: Suitable for scenarios where software is used intermittently by multiple people (e.g., labs, call centers).
- Example: Licensing models for software used by multiple departments, such as AutoCAD or Microsoft SQL Server.
Device licenses:
- Per-device usage: Licenses are tied to specific devices (computers, servers, or other hardware).
- Common for embedded systems: Often used for software installed on specific devices, such as medical equipment or IoT devices.
- Example: Software installed on dedicated servers or devices with embedded systems (e.g., device management software for printers).
2. Open-source licenses
- Varying levels of freedom: Open-source licenses grant varying degrees of freedom to use, modify, and distribute the software. They are generally not tied to commercial payments, but they can have stipulations depending on the license.
- Examples:
- GPL (GNU General Public License): Requires that any modifications or derivatives of the software also be open-source.
- MIT License: Very permissive, allowing for commercial use and modification with minimal restrictions.
- Apache License 2.0: Allows commercial use and modification with attribution, Widely used for commercial and open-source projects.
- BSD License: Another permissive open-source license with minimal restrictions, often used in academic and commercial projects.
3. Freeware licenses
Free to use: Freeware software is available at no cost, but may come with limitations. These limitations might include restricted features or certain conditions of use.
- Common restrictions:
- Limited functionality or features (e.g., free versions with premium upgrades).
- Displaying advertisements.
- May restrict commercial use or redistribution.
- Example: Basic tools like Avast Antivirus (free version), or simple apps like GIMP (open-source but often used as freeware).
4. Shareware licenses
- Trial period: Shareware allows users to try the software for a limited time or with restricted features.
- Requires purchase for full functionality: After the trial period or limited functionality expires, users must purchase a license to continue using the software with full features.
- Common characteristics:
- Often comes with a feature set that is "locked" until purchase (e.g., limitations on saving, exporting, or usage time).
- Encourages users to try before they buy.
- Example: Early versions of software like WinRAR, or popular games that offer "trial versions" or "freemium" models (e.g., Adobe Creative Cloud trial).
Software license management tool acts as a safeguard, ensuring that organizations use commercial proprietary software legally, efficiently, and securely.
Benefits of using Software License Management tool
In today's technology-driven landscape, effective software license management is no longer an option, but a necessity. By strategically managing software licenses, organizations can significantly reduce costs, mitigate risks, and improve overall operational efficiency.
1. Enhanced software license compliance and reduced legal risks
- Minimizing Audit Risk: Software vendors often conduct audits to ensure compliance with licensing agreements. License management tools provide real-time visibility into software usage, helping organizations identify and address potential compliance issues before they escalate. This significantly reduces the risk of costly fines and legal penalties associated with non-compliance. Proactive license compliance ensures organizations are prepared for potential software vendor audits.
- Preventing Legal Disputes: Adhering to licensing agreements is crucial for maintaining positive relationships with software vendors. By ensuring compliance, organizations can avoid legal disputes, potentially leading to better pricing, improved support, and access to exclusive benefits.
2. Cost Optimization & Resource Efficiency
- Identifying and Reclaiming Unused Licenses: Software license management tools help identify unused or underutilized software licenses, allowing organizations to reclaim valuable resources and reduce unnecessary spending.
- Optimizing Software Investments: By accurately tracking software usage patterns, organizations can make data-driven decisions about software purchases, ensuring they invest in the right tools and maximizing their return on investment (ROI).
3. Increased Operational Efficiency & Productivity
- Streamlining IT Operations: Automating software license management processes, such as license discovery, tracking, and renewal, frees up valuable IT resources for more strategic initiatives.
- Improving IT Productivity: By reducing the time spent on manual license management tasks, IT teams can focus on improving IT infrastructure, enhancing security, and providing better support to end-users.
4. Proactive Renewal Management & Business Continuity
- Preventing Service Disruptions: Automated renewal reminders and alerts ensure timely renewals of software licenses, minimizing the risk of service interruptions and ensuring business continuity.
- Negotiating Better Terms: By leveraging data on software usage and renewal history, organizations can negotiate more favorable terms with software vendors, potentially securing discounts, extended support, or additional benefits.
5. Enhanced Audit Preparedness & Improved Governance
- Generating Comprehensive Audit Reports: Software license management solutions generate detailed reports on software inventory, usage, and compliance, providing the necessary documentation for successful audits.
- Improving IT Governance: By establishing clear policies and procedures for software acquisition and usage, software license management contributes to improved IT governance and demonstrates a commitment to responsible software practices.
Implementing a robust software license management strategy is crucial for any organization that relies on software to function effectively. By embracing these key benefits, businesses can gain greater control over their software investments, reduce costs, enhance security, and improve overall operational efficiency.
Use Cases of Software License Management
1. Healthcare:
- Improving HIPAA Compliance: Healthcare organizations must comply with strict regulations like HIPAA, which requires them to protect patient data. Effective software license management ensures that all software used to handle sensitive patient information is properly licensed and compliant with security standards.
- Optimizing Medical Imaging Software: Medical imaging software is often expensive and subject to complex licensing agreements. License management helps hospitals and clinics track usage, ensure compliance, and optimize costs associated with these critical tools.
- Maintaining EHR Systems: Electronic Health Record (EHR) systems are essential for modern healthcare. Software license management ensures that these systems are properly licensed, updated, and maintained to ensure data security and patient care continuity.
2. Education:
- Streamlining Campus-Wide Software Management: Educational institutions often have a diverse range of software needs, from classroom management tools to research software. License management helps universities and schools track licenses, ensure compliance, and optimize software spending across the entire campus.
- Providing Students with Secure Software Access: Software license management ensures that students have access to the necessary software for their studies, whether it's design software, programming languages, or research tools, while maintaining a secure and compliant environment.
- Improving Compliance with Educational Software Licensing Agreements: Many educational software vendors have specific licensing agreements for institutions. Software license management helps ensure compliance with these agreements and avoid potential legal issues.
3. Finance:
- Managing Trading and Investment Software with License Management: Financial institutions rely heavily on specialized software for trading, investment analysis, and risk management. Software license management helps ensure that these critical systems are properly licensed, updated, and secure.
- Enhancing Compliance with Financial Regulations: The financial industry is subject to strict regulations. License management helps financial institutions demonstrate compliance with relevant regulations and maintain a strong audit trail.
- Protecting Sensitive Financial Data with License Management: By ensuring that all software used to handle financial data is properly licensed and up-to-date, organizations can minimize the risk of data breaches and security vulnerabilities.
4. Manufacturing:
- Optimizing Industrial Automation Software with License Management: Manufacturing processes often rely heavily on automation software, such as PLCs (Programmable Logic Controllers) and SCADA systems. Software license management helps manufacturers track licenses for these critical systems, ensure compliance with vendor agreements, and minimize downtime.
- Improving Production Efficiency with License Management: By effectively managing licenses for manufacturing software, organizations can optimize production processes, improve efficiency, and reduce costs.
- Enhancing Data Security in Industrial Environments with License Management: Industrial environments often contain sensitive data, such as production schedules and intellectual property. License management helps ensure that all software used in these environments is secure and compliant with relevant security standards.
5. Government:
- Improving Compliance with Government Regulations with License Management: Government agencies are subject to strict regulations regarding software procurement and usage. License management helps government agencies ensure compliance with these regulations and avoid potential penalties.
- Managing Mission-Critical Software with License Management: Government agencies rely on a wide range of mission-critical software, from cybersecurity tools to communication systems. License management helps ensure that these systems are properly licensed, updated, and secure.
- Optimizing IT Spending with License Management: Government budgets are often constrained. Effective software license management helps government agencies optimize IT spending and ensure that taxpayer dollars are used efficiently.
How Software License Management Empowers Your Teams
1. IT Administrators:
- Streamline Software Deployments: Gain visibility into software usage and license availability, enabling faster and more efficient software deployments across the organization.
- Enhance Software Security: Identify and mitigate security risks associated with unlicensed or outdated software.
- Reduce IT Support Costs: Minimize the number of IT support requests related to software installations, updates, and access issues.
2. Procurement Teams:
- Optimize Software Spending: Identify areas for cost optimization by identifying unused or underutilized licenses and negotiating better deals with vendors.
- Make Data-Driven Purchasing Decisions: Leverage usage data to make informed decisions about software purchases, ensuring that investments align with business needs.
- Improve Budget Forecasting: Accurately forecast future software needs and budget accordingly.
3. Compliance Officers:
- Simplify Audit Preparation: Generate comprehensive compliance reports to streamline audit preparation and demonstrate compliance with software vendor agreements and internal policies.
- Minimize Audit Risk: Proactively identify and address potential compliance issues, reducing the risk of costly fines and legal penalties.
- Ensure Regulatory Compliance: Demonstrate compliance with relevant regulations and industry standards.
What is Software License Compliance?
Software License Compliance refers to the practice of ensuring that an organization is using software in accordance with the terms and conditions outlined in the relevant software license agreements. This includes:
- Using the correct number of licenses: Ensuring that the number of software installations and users does not exceed the number of licenses purchased.
- Adhering to usage restrictions: Complying with any limitations on usage, such as the number of concurrent users, geographic restrictions, or permitted use cases.
- Maintaining proper documentation: Keeping accurate records of all software licenses, including purchase orders, invoices, and license keys.
Why is Software Compliance Important for Enterprises?
- Avoiding Legal and Financial Penalties: Non-compliance with software licenses can result in significant legal and financial consequences, including:
- License audits: Software vendors may conduct audits to verify license compliance, which can be costly and disruptive.
- Fines and penalties: Non-compliance can result in hefty fines and penalties imposed by software vendors.
- Legal action: In some cases, non-compliance can lead to legal action, including lawsuits and injunctions.
- Maintaining a Positive Vendor Relationship: Compliance demonstrates respect for intellectual property rights and fosters a positive relationship with software vendors, potentially leading to better pricing, improved support, and access to exclusive benefits.
- Protecting Brand Reputation: Non-compliance can damage an organization's reputation and erode customer trust.
- Ensuring Business Continuity: Using unlicensed software can expose organizations to security risks, data breaches, and system instability, potentially disrupting business operations.
- Improving Operational Efficiency: By ensuring that software is used efficiently and effectively, organizations can optimize their software investments and reduce costs.
Key Steps to Ensure Software Compliance:
- Conduct a Software Inventory: Identify all software installed across the organization.
- Review Software Licenses: Analyze all software licenses to understand the terms and conditions.
- Track Software Usage: Monitor software usage patterns to identify potential compliance issues.
- Implement a Software License Management System: Utilize tools and processes to automate license tracking, manage renewals, and ensure compliance.
- Conduct Regular Audits: Regularly review software usage and compliance to identify and address any potential issues.
- Train Employees: Educate employees about software licensing and the importance of compliance.
By using a comprehensive software license management solution, enterprises can mitigate risks, reduce costs, and maximize the value of their software investments.
FAQ
-
What is Software License Management?
Software License Management is the process of tracking, controlling, and optimizing the use of software licenses within an organization. It involves activities like:
- Software Discovery: Identifying all software installed across the organization.
- License Inventory: Maintaining an accurate record of all software licenses (type, quantity, expiration dates).
- Usage Monitoring: Tracking how software is being used across the organization.
- Compliance Enforcement: Ensuring adherence to software license agreements.
- Cost Optimization: Identifying and eliminating wasteful spending on software.
-
Why is Software License Management Important?
- Reduces Costs: Avoids overspending on software, identifies and reclaims unused licenses.
- Enhances Compliance: Minimizes the risk of software audits, fines, and legal penalties.
- Improves Security: Reduces the risk of using unlicensed or outdated software, which can have security vulnerabilities.
- Increases Efficiency: Streamlines IT operations, freeing up valuable IT resources.
- Better Decision-Making: Provides data-driven insights for informed software purchasing decisions.
-
What are the Different Types of Software Licenses?
- Perpetual Licenses: One-time purchase, ongoing use.
- Subscription Licenses: Recurring payments for ongoing use.
- Named User Licenses: Licenses assigned to specific individuals.
- Concurrent User Licenses: Allows a specific number of users to access software simultaneously.
- Device Licenses: Licenses tied to specific devices.
- Open-Source Licenses: Varying degrees of freedom to use, modify, and distribute.
-
What are the Key Features of a Software License Management Tool?
- Centralized License Repository: Stores all license information.
- License Utilization Tracking: Monitors software usage patterns.
- Automated Renewals: Provides reminders and alerts for upcoming renewals.
- Compliance Monitoring: Identifies and addresses potential compliance issues.
- Cost Optimization: Tracks spending and identifies areas for cost savings.
- Reporting & Analytics: Generates reports for analysis and decision-making.
- User Access Control: Controls access to license data based on user roles.
-
How Can I Get Started with Software License Management?
- Conduct a Software Inventory: Identify all software installed across the organization.
- Review Existing Licenses: Analyze all software license agreements.
- Implement a Software License Management Tool: Choose and implement a suitable tool.
- Train Employees: Educate employees on software licensing policies and procedures.
- Conduct Regular Audits: Regularly review software usage and compliance.
-
What are the Benefits of Using a Software License Management Tool?
- Improved compliance and reduced audit risk.
- Cost optimization and reduced software spending.
- Increased operational efficiency and IT productivity.
- Enhanced security and reduced risk of data breaches.
- Better decision-making based on data-driven insights.
Explore additional IT Asset Management features
Disover the essential features and functionalities of Zecurit Asset Manager.
Asset Discovery
Automatically discover all IT assets across your network for complete inventory visibility.
Software Inventory
Track all software installations and ensure accurate license utilization to avoid costly audits.
Hardware Inventory
Track all hardware assets, from desktops to servers, for effective monitoring and proactive maintenance.
Software License Management
Manage software licenses effectively, reduce costs, and ensure compliance with vendor agreements.
Software Metering
Monitor software usage in real-time to optimize license utilization and maximize your software investments.
CMDB
Centralize IT infrastructure configuration information for improved incident response and streamlined change management.