Understanding EDR, MDR, and XDR:
Differences and Choosing the Best Option
Compare EDR, MDR, and XDR capabilities to make informed decisions on advanced threat detection, response, and managed defense.
In today’s dynamic cybersecurity landscape, organizations face an ever-evolving array of threats, making robust detection and response strategies essential. Among the most widely discussed solutions are Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR), Managed Detection and Response (MDR), and Extended Detection and Response (XDR). Understanding the distinctions among these options is crucial for businesses seeking to strengthen their security posture effectively.
What is EDR?
Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) focuses on monitoring and securing endpoint devices within a network. These include laptops, desktops, and servers, devices often targeted by cyberattacks. EDR solutions use software agents installed on these endpoints to continuously gather and analyze data in real-time. This allows for the rapid detection of suspicious activities and potential threats.
Key Features of EDR:
- Real-Time Monitoring: Provides constant surveillance of endpoint activities.
- Behavioral Analysis: Leverages Indicators of Compromise (IOCs) and Indicators of Attack (IOAs) to detect anomalous behaviors.
- Remediation Recommendations: Offers actionable insights to help security teams address incidents efficiently.
EDR is best suited for organizations with skilled in-house security teams capable of managing the tools and responding to threats effectively.
What is MDR?
Managed Detection and Response (MDR) builds upon the capabilities of EDR by incorporating outsourced security services. MDR combines advanced technology with human expertise to deliver 24/7 monitoring and response capabilities. This solution is particularly beneficial for organizations that lack the resources or expertise to manage security operations internally.
Key Aspects of MDR:
- 24/7 Monitoring: Provides around-the-clock oversight by a team of experienced security professionals.
- Threat Hunting: Proactively searches for threats across the organization’s network.
- Incident Response: Ensures rapid identification, containment, and remediation of threats without requiring in-house staffing.
MDR is an excellent choice for smaller organizations or those without dedicated security teams.
What is XDR?
Extended Detection and Response (XDR) is an evolution of EDR, offering broader visibility by integrating data from multiple sources beyond just endpoints. It consolidates information from networks, cloud services, and other security tools to provide a holistic view of an organization’s security posture.
Main Features of XDR:
- Unified Security Approach: Integrates data from diverse sources for enhanced visibility and context.
- Enhanced Threat Detection: Correlates data across multiple platforms to identify sophisticated threats.
- Automated Responses: Simplifies and accelerates incident response through automation.
XDR is ideal for organizations with complex IT environments facing advanced and multi-faceted cyber threats.
Key Differences Between EDR, MDR, and XDR
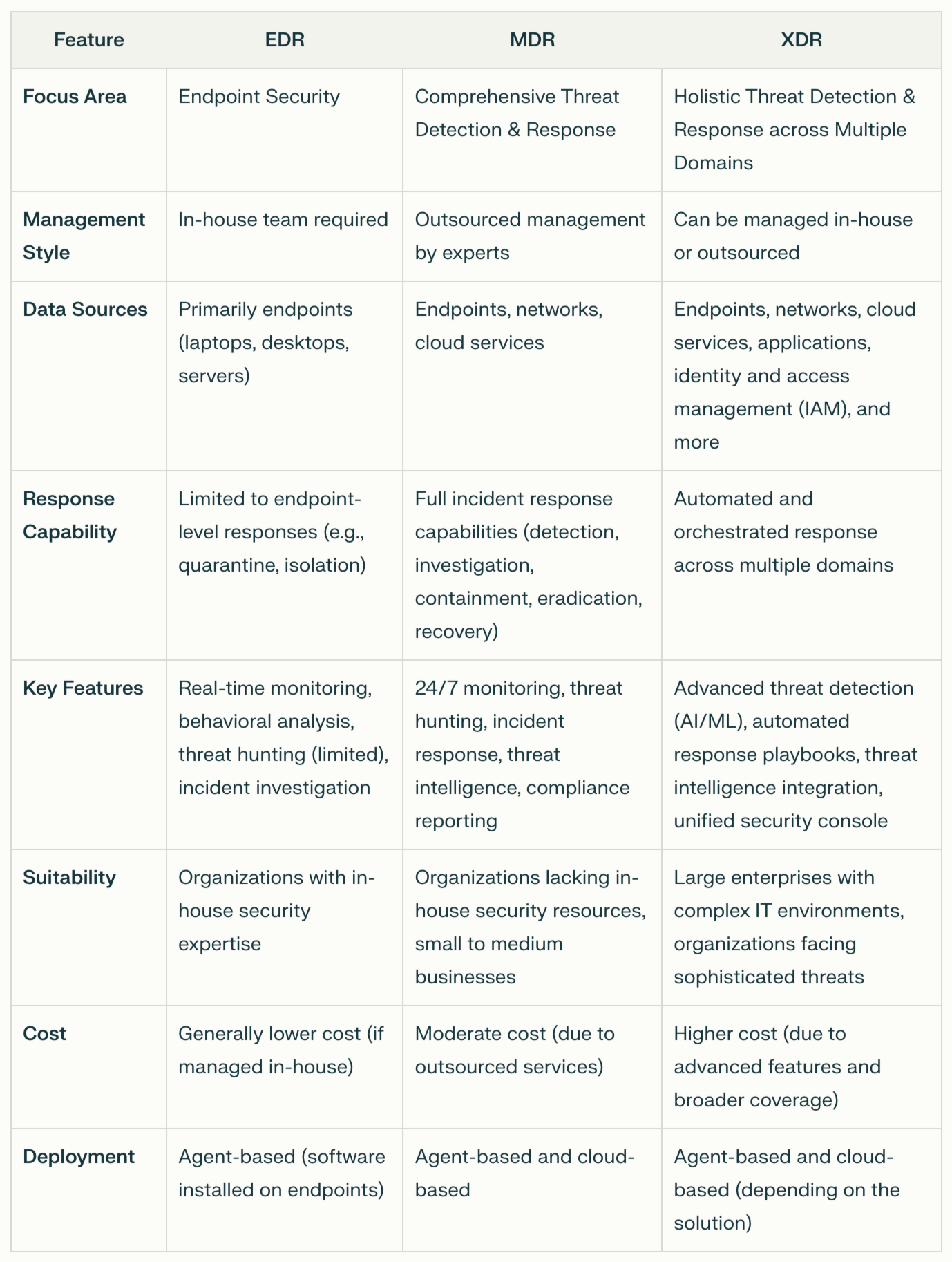
Choosing the Best Option
When deciding between EDR, MDR, and XDR, organizations should evaluate several factors:
Organizational Size
- Smaller organizations may benefit more from MDR due to its expert management without requiring a large in-house team.
- Larger organizations with complex IT environments might find XDR more suitable because of its extensive coverage and integration capabilities.
In-House Expertise
- Companies with skilled cybersecurity teams can manage EDR effectively and benefit from its cost-efficiency.
- Organizations lacking such expertise should consider MDR for access to professional management and resources.
Threat Landscape Complexity
- Businesses facing sophisticated threats across multiple environments should opt for XDR, as it provides a unified view of attack vectors and better detection capabilities.
Budget Considerations
- EDR is a cost-effective solution when managed in-house but may require significant investment in personnel.
- MDR involves higher costs due to outsourcing but delivers 24/7 expert support.
- XDR, while potentially the most expensive, offers extensive capabilities that justify the investment for organizations with complex needs.
Top Vendors in EDR, MDR, and XDR
Choosing the right vendor is crucial for effective threat protection. Here are some of the leading players:
EDR Vendors
- CrowdStrike Falcon: Known for its cloud-native platform and strong AI/ML capabilities.
- SentinelOne Singularity: Offers a unified XDR platform with advanced threat hunting and response features.
- Microsoft Defender for Endpoint: Leverages deep integration with the Microsoft ecosystem for comprehensive protection.
- Cybereason Defense Platform: Offers a unique behavioral analytics engine for advanced threat detection.
Please check out: Top EDR tools on the market.
MDR Vendors
- eSentire: A leading MDR provider with a global threat intelligence network.
- Rapid7 InsightIDR: Combines MDR with SIEM and SOAR capabilities for comprehensive security operations.
- Huntress: Specializes in managed threat hunting services, focusing on proactive threat detection.
- ReliaQuest GreyMatter: Offers a platform for automating security operations and integrating with various security tools.
XDR Vendors
- Microsoft Defender XDR: Integrates with Microsoft's security portfolio for comprehensive threat protection.
- Trend Micro Vision One: Offers a cloud-native XDR platform with advanced threat detection and response capabilities.
- Palo Alto Networks Cortex XDR: Provides a unified platform for detecting and responding to threats across networks, endpoints, and cloud environments.
- Cisco SecureX: Offers a cloud-based security platform that integrates with Cisco's security portfolio and third-party tools.
Choosing the right vendor depends on your specific needs and budget. Consider factors such as the level of threat protection required, the desired level of automation, and the need for managed services. It's recommended to evaluate multiple vendors and conduct thorough proof-of-concept tests before making a decision.
Conclusion
In summary, EDR, MDR, and XDR each play unique roles in an organization’s cybersecurity strategy. By understanding their differences in focus areas, management styles, data sources, and response capabilities, businesses can make informed decisions tailored to their specific requirements. Ultimately, the choice will depend on factors such as organizational size, in-house expertise, threat landscape complexity, and budget. Selecting the right solution ensures a stronger and more resilient security posture in an ever-changing cyber threat environment.
Related Articles:
Frequently asked questions:
-
What are the primary differences between EDR, MDR, and XDR?
EDR focuses on securing endpoint devices like laptops and servers, requiring an in-house security team to manage alerts and responses.
MDR combines EDR technology with outsourced 24/7 monitoring and response services, making it ideal for organizations without in-house expertise.
XDR extends beyond endpoints, integrating data from networks, cloud environments, and other sources to provide a holistic security view, suitable for complex IT environments.
-
Which option is most cost-effective for a small organization?
MDR is often the most cost-effective choice for small organizations. It provides expert management, 24/7 monitoring, and comprehensive threat response without requiring a dedicated in-house security team.
-
How does XDR improve threat detection compared to EDR?
XDR improves threat detection by correlating data from multiple sources, such as endpoints, networks, and cloud services, offering a unified view. This broader integration helps identify complex, multi-faceted threats that might go unnoticed with endpoint-focused EDR solutions.
-
Can EDR be a standalone solution for organizations?
Yes, EDR can be a standalone solution, but it requires a skilled in-house security team to manage alerts, analyze threats, and respond effectively. Organizations without sufficient expertise may struggle to utilize EDR to its full potential.
-
What factors should an organization consider when choosing between EDR, MDR, and XDR?
Key Factors to Consider
- Organizational Size:
- Smaller teams may prefer MDR.
- Larger organizations with complex IT setups might benefit from XDR.
- In-house Expertise:
- EDR is suitable if the organization has skilled security professionals.
- Threat Complexity:
- XDR is better for detecting advanced threats across multiple environments.
- Budget:
- EDR is cost-effective for those with in-house capabilities.
- MDR and XDR incur additional costs for outsourced expertise or broader coverage.
- Organizational Size: