Remote Desktop is a technology that enables users to access and control a computer or server from a different location over a network, facilitating remote work, technical support, and system administration.

In today's digital age, remote work and access to systems from anywhere have become essential. Whether you're working from home, traveling, or managing a remote team, the need to access a computer or server located elsewhere is increasingly common. This is where the concept of Remote Desktop comes into play.
A Remote Desktop is a technology that allows a user to connect to a computer or server from a distant location and use it as if they were physically sitting in front of it. This means that you can access a machine’s desktop, files, applications, and other resources remotely via the internet or local network.
In simpler terms, it’s like taking control of another computer from a different location, using your own device.
The core idea behind remote desktop technology is that it creates a virtual environment, known as a "session," that allows you to interact with a computer from a different physical location.
Here’s how it works, step by step:
There are several different remote desktop technologies available, each with varying features, levels of performance, and security.
The most widely known and used protocol is RDP, which is built into Windows operating systems. RDP is a proprietary protocol developed by Microsoft and allows users to connect to a Windows-based computer or server. RDP is known for its strong security features, including encryption, and it supports multiple users simultaneously.
VNC is another popular protocol used for remote access. It works across multiple operating systems, including Windows, macOS, and Linux. Unlike RDP, VNC is an open-source protocol, which means it can be customized to suit specific needs.
Several third-party remote desktop applications have gained popularity, especially for users needing remote access across different devices and operating systems. Some of the most commonly used are:
TeamViewer: Known for its ease of use and robust features like file sharing, remote printing, and cross-platform support (Windows, macOS, Linux, iOS, Android).
AnyDesk: Another lightweight option offering good performance with low latency, useful for both personal and business use.
Chrome Remote Desktop: A browser-based solution that allows remote access via Google Chrome, free and easy to use for individuals.
Cons: Some are paid services, and their security and privacy policies may vary.
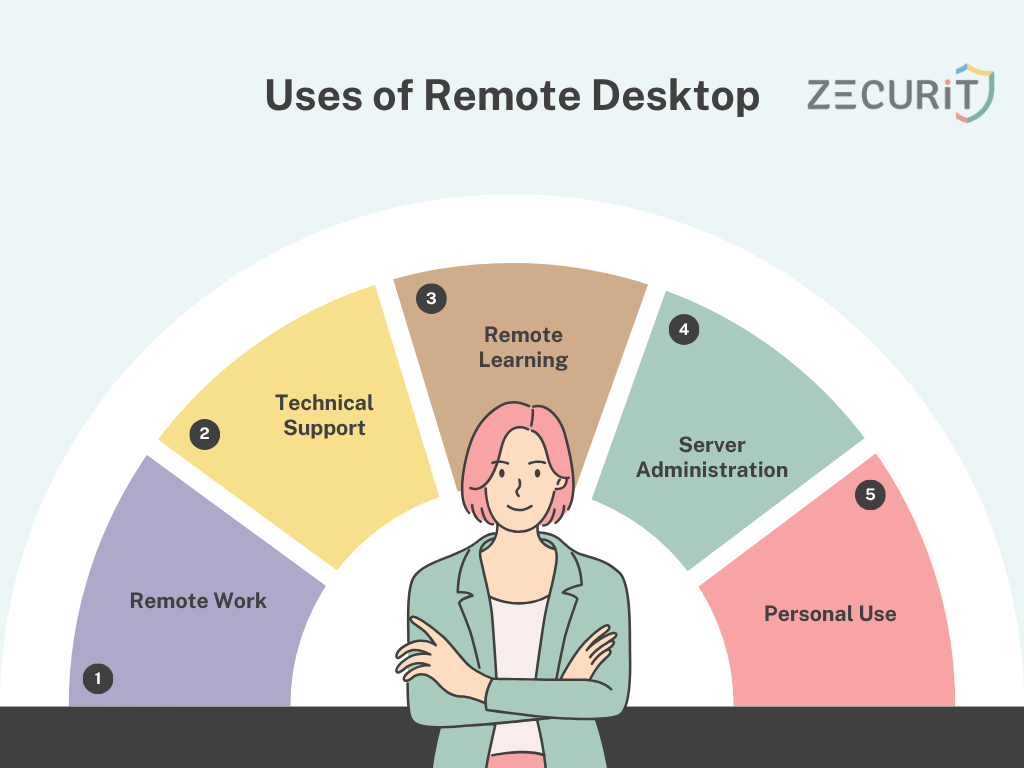
Remote desktop technology is used in a variety of scenarios:
Remote Work: With the rise of remote work, employees use remote desktops to access their work machines, software, and files from their home or anywhere with internet access.
Technical Support: IT professionals often use remote desktop tools to troubleshoot and fix issues on a user's computer, whether for personal or corporate support.
Remote Learning: Educational institutions may use remote desktops to provide access to software or systems that students need, such as specialized design or engineering applications.
Server Administration: System administrators often use remote desktop protocols to manage and maintain servers located in data centers or remote offices.
Personal Use: You can access your home computer from anywhere, ensuring that you have access to your files and applications while you're on the go.
As long as you have an internet connection, you can access your remote desktop from virtually anywhere in the world. This flexibility is especially beneficial for workers who travel frequently or work from home.
For businesses, remote desktop technology can help save money by reducing the need for on-site IT support. Instead, IT teams can solve problems remotely. It also enables businesses to support remote work, which can reduce office space and operational costs.
Remote desktop technology allows IT departments to centrally manage and maintain multiple machines, ensuring updates and patches are applied across all systems. This centralized approach improves efficiency and security.
Most remote desktop software encrypts the connection between the client and host, adding an extra layer of security to sensitive data. Some solutions also offer multi-factor authentication (MFA), which helps ensure that only authorized users can access the system.
While remote desktops offer significant advantages, they do come with certain challenges:
Connection Quality: Remote desktop performance is heavily dependent on the quality of the internet connection. A slow or unstable connection can lead to latency, poor image resolution, and a frustrating user experience.
Security Risks: While encryption is used, remote desktop services are still susceptible to cyber-attacks like brute force attacks, phishing, or unauthorized access if proper security measures are not in place. Keeping software updated and using strong passwords or multi-factor authentication is crucial.
Licensing Fees: Some remote desktop solutions, particularly enterprise-level tools, may have licensing or subscription fees, which can be expensive depending on the number of users.
Complex Setup for Remote Access: Setting up a remote desktop connection, especially for access over the internet (beyond local networks), can sometimes be complicated, involving port forwarding, firewall configuration, and VPN setup.
Remote desktop technology has revolutionized the way we interact with computers, enabling users to work, collaborate, and manage systems from virtually anywhere. It is an essential tool for businesses, IT professionals, and anyone who needs to access remote resources. Whether you're connecting to a work computer, assisting a colleague with troubleshooting, or simply accessing personal files while traveling, remote desktop makes it possible.
With the increasing reliance on remote work and distributed teams, mastering remote desktop tools and understanding the protocols involved will continue to be an important skill in the modern digital landscape.
Remote Desktop is a technology that allows users to access and control a computer or server from a different location over the internet or a local network.
Remote desktop works by establishing a secure connection between the client device (like a laptop or smartphone) and the host computer, allowing the user to control it as if they were physically present.
The main types are RDP (Remote Desktop Protocol), VNC (Virtual Network Computing), and third-party solutions like TeamViewer, AnyDesk, and Chrome Remote Desktop.
Remote Desktop allows access to a computer from anywhere, centralized management of IT resources, cost savings, and enhanced security with encrypted connections.
Challenges include poor connection quality, security risks if not properly configured, potential setup complexity, and licensing fees for some advanced solutions.
FEATURES
SOLUTIONS
EXPLORE REMOTE ACCESS